According to the National Institutes of Health, 1.3 million people In the United States begin to experience symptoms of menopause each year, usually characterized by feelings of intense heat known as hot flashes. Menopause can last for years, and the associated temperature swings are uncomfortable at best and debilitating at worst. Because there’s no definitive cure for these biological responses, a textile marketer named Louise Nicholson wanted to help people stay comfortable during this period of their lives. However, she found existing options lacking – until she came across a material born from NASA funding.
“I did some initial research to find out what was on the market, and there was absolutely nothing apart from nightwear,” Nicholson said.
Exploring high tech fabrics for regulating temperatures, Nicholson found that these products tended to be cooling fabrics, which ignored the cold flashes that often follow hot flashes. Her search soon brought her to a technology called Outlast.
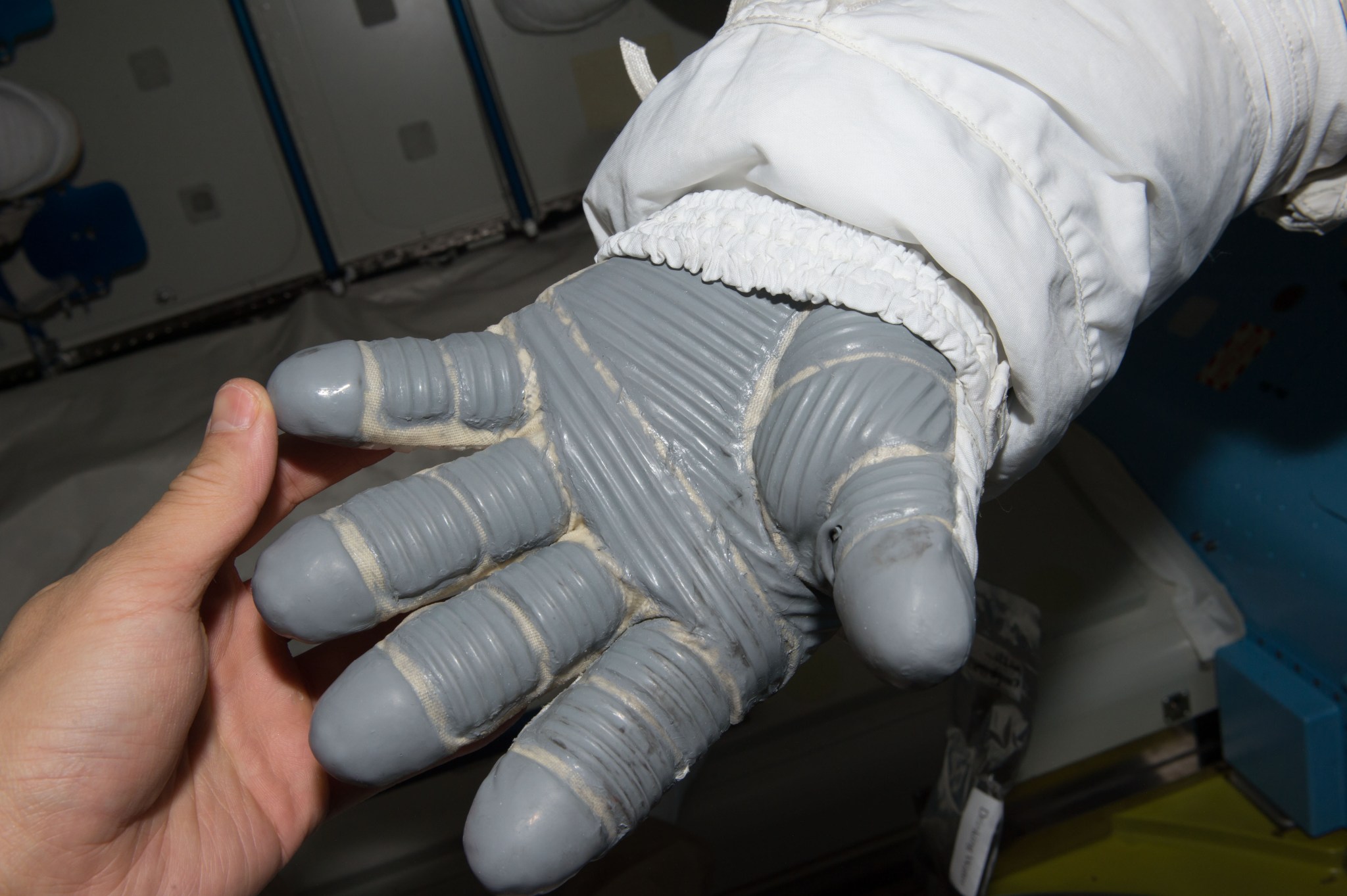
In the 1980s, NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston was looking for ways to improve insulation in spacesuit gloves. The center entered into a Small Business Innovation Research contract with the Triangle Research and Development Corporation to explore the use of phase-change materials, which maintain a steady temperature as they change phase from solid to liquid or vice-versa. Based on earlier work it had done with the U.S. Air Force, by embedding phase-change materials into microcapsules inside the material, Triangle was able to demonstrate the effectiveness of a temperature-stabilizing fabric insert for a spacesuit glove. While the technology never went into space, Gateway Technologies (later known as Outlast Technologies) acquired exclusive patent rights from Triangle and soon began marketing it under the name Outlast.
Outlast has been used in numerous products, from desk chairs to underwear. Walero, which uses the material in clothes for race car drivers, had sold some of its Outlast apparel to people experiencing menopause, but Nicholson noticed that there didn’t seem to be any brands using this technology specifically for menopause.
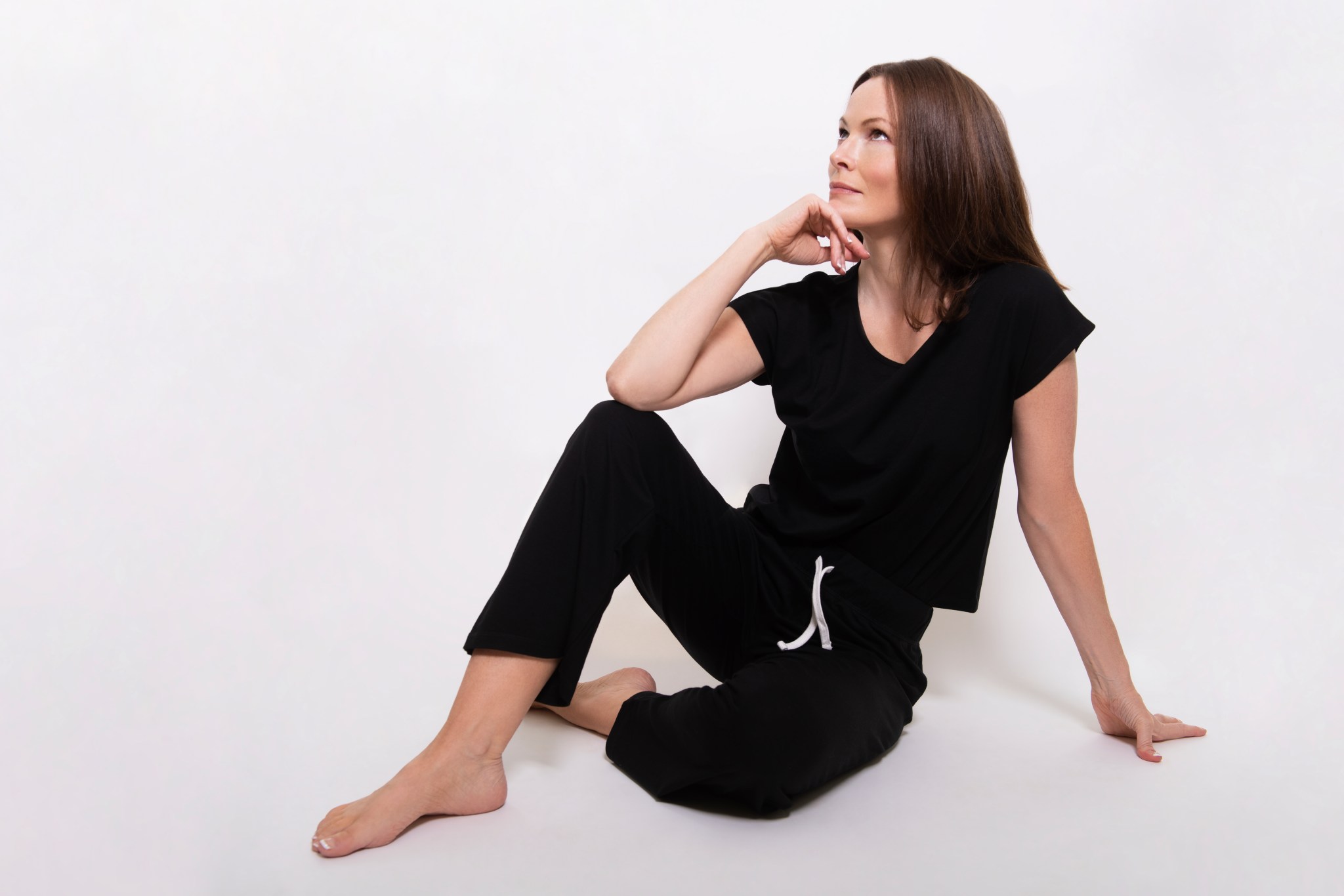
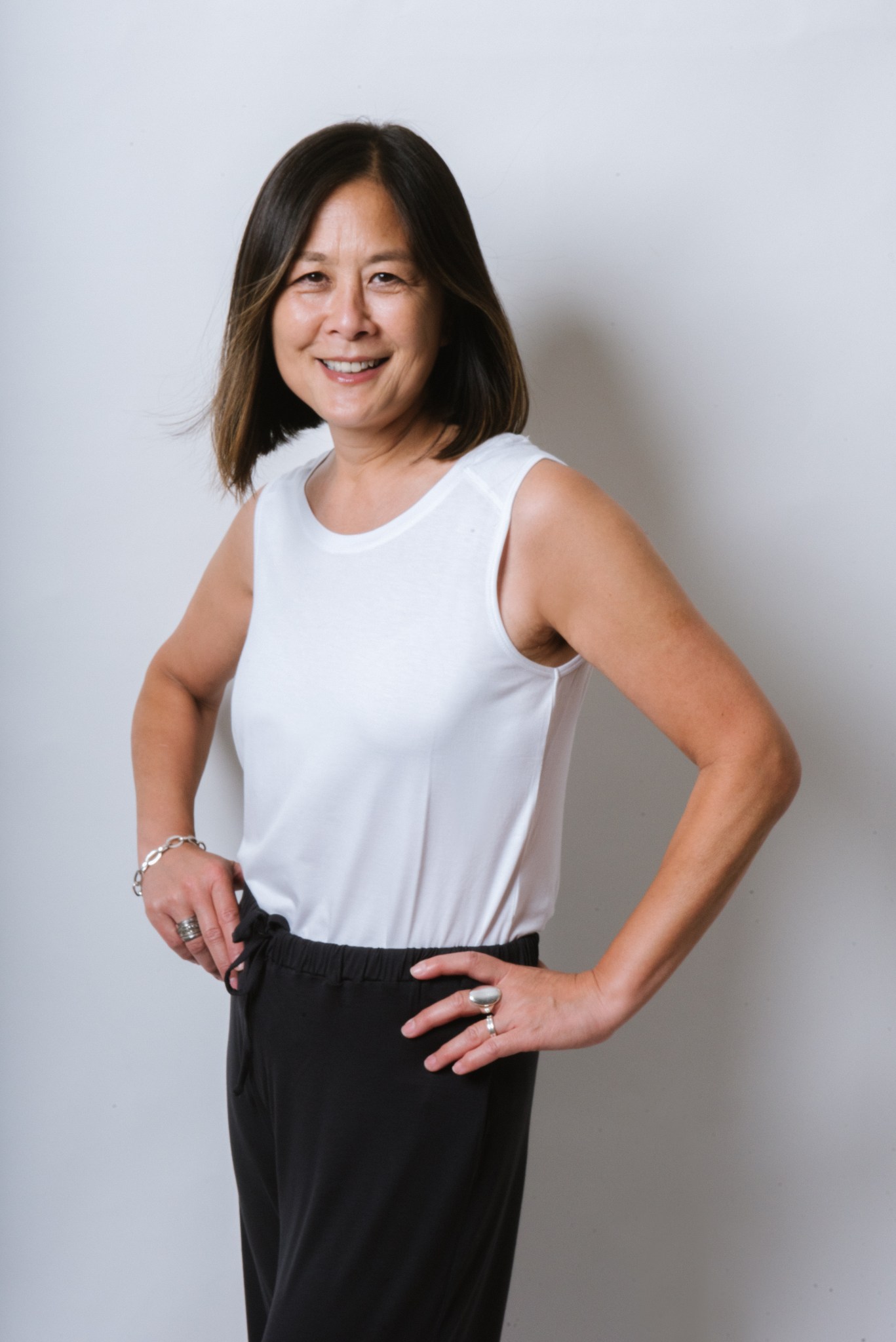
Founded by Nicholson in 2017, London-based Fifty One Apparel is named after the average age when people can begin to experience menopause. By bonding Outlast to cellulosic yarn, the company’s clothing maintains the temperature-regulating properties of phase-change materials but retains the look and feel of high-end fabrics.
The initial products, a line of shirts in four styles were first sold to consumers in the London area via parties, but the company has expanded to e-commerce, selling tops, bottoms, and nightwear directly to individuals around the world. As of 2021, the United States is Fifty One’s second-largest market after the United Kingdom, and the company is looking to obtain a local distributor for the product. In addition, Fifty One has expanded its range of Outlast-based products, including accessories like scarves, facemasks, and turbans.
NASA has a long history of transferring technology to the private sector. The agency’s Spinoff publication profiles NASA technologies that have transformed into commercial products and services, demonstrating the broader benefits of America’s investment in its space program. Spinoff is a publication of the Technology Transfer program in NASA’s Space Technology Mission Directorate (STMD).
For more information on how NASA brings space technology down to Earth, visit:
By Andrew Wagner
NASA’s Spinoff Publication